What is Fixed capital? Definition, Meaning and Examples
 Definition of Fixed Capital
Definition of Fixed Capital
In general, the definition of fixed capital can be stated as under.
“Fixed capital is a compulsory initial investment made by the entrepreneur to start up the activities of his business.”
Fixed capital is a mandatory one-time investment made at the introductory phase of a business establishment.
Fixed capital is not alike working capital, which is required on a continuous basis to operate (run) the ordinary course of production and distribution of goods and services.
Image credits © Vip223.
According to Hoagland,
“Fixed capital is comparatively easily defined to include land, building, machinery and other assets having a relatively permanent existence.”
Fixed capital is a permanent investment made to meet the longer-term needs (requirements) of the business activities.
Thus, fixed capital has a permanent existence in the business. It is usually present in the form of fixed assets like land, building, plant, machinery, etc.
 Meaning of Fixed Capital
Meaning of Fixed Capital
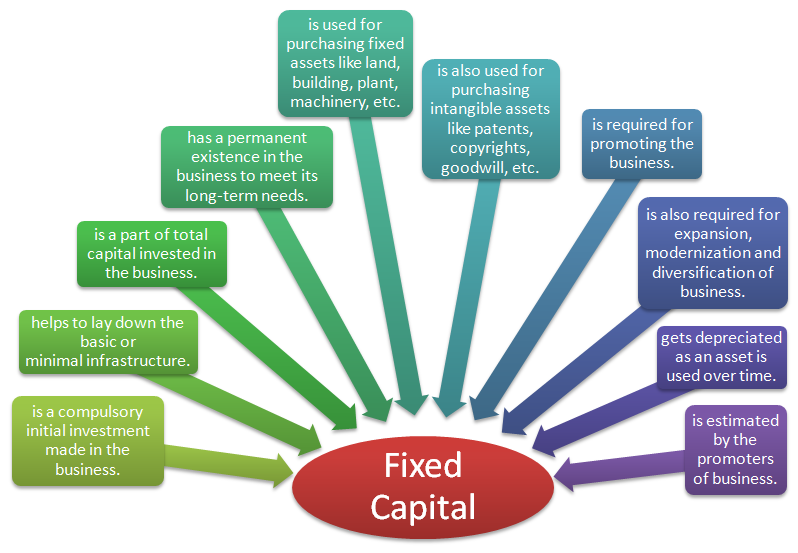
The meaning of fixed capital is depicted in the following chart.
The meaning of fixed capital can be easily grasped from these points:
- Fixed capital is a compulsory initial investment made in the business.
- It helps to lay down the basic infrastructure on which business is supposed to stand and flourish in a long run.
- It is a part of total capital invested in the business.
- It has a permanent existence in the business to meet its long-term needs.
- It is used for purchasing fixed assets like land, building, plant, machinery, etc.
- It is also used for purchasing intangible assets like patents, copyrights, goodwill, etc.
- It is required for promoting the business.
- It is also required for expansion, modernization and diversification of business.
- Fixed capital gets depreciated as an asset is used over time with few exceptions like in case of land.
- Fixed capital requirement is estimated by the promoters of business. This estimation must be made as accurately as possible. To achieve this, the promoters seek professional help and take advice from experts such as engineers, architects, etc.
Read following articles to know more on the concept of fixed capital:
- Features of fixed capital
- Role or importance of fixed capital
- Sources of fixed capital
- Factors affecting fixed capital requirement
 Examples of Fixed Capital
Examples of Fixed Capital
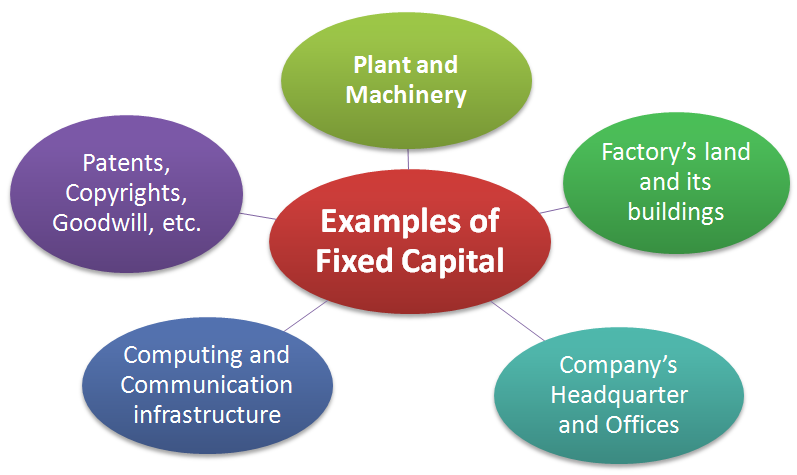
The examples of fixed capital are depicted in the following image.
Common examples of fixed capital investments are as follows:
- Plant and machinery.
- Factory's land and its buildings.
- Company's headquarter (HQ), administrative areas, regional and local offices, and their premises.
- Computing and communication infrastructure that mostly includes workstations, servers, data-storage facilities, local-area networks, the internet, telephones, fax, so on.
- Patents, copyrights, goodwill, etc., also gets covered under fixed capital.

No Comment Yet
Please Comment